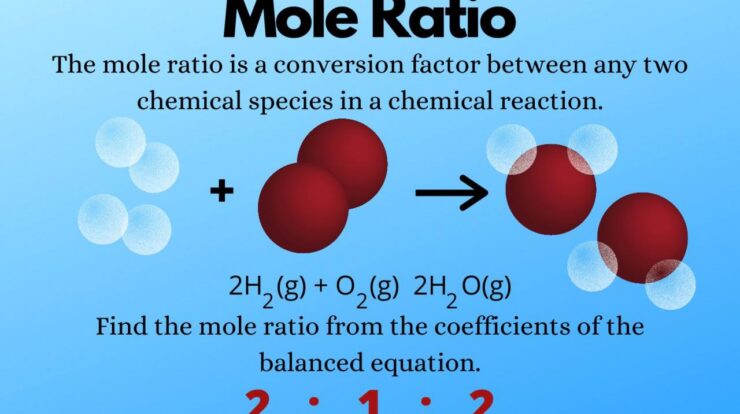
Mole measurement, a fundamental concept in chemistry, plays a pivotal role in understanding chemical reactions and stoichiometry. By quantifying the amount of substance, mole measurement empowers chemists to analyze, predict, and manipulate chemical processes with precision.
The concept of a mole, defined as the amount of substance that contains exactly 6.022 x 10^23 elementary entities, provides a universal reference point for chemical calculations. This measurement enables scientists to determine the molar mass of substances, calculate the number of atoms or molecules present, and predict the products and quantities involved in chemical reactions.
Definition and Importance of Mole Measurement
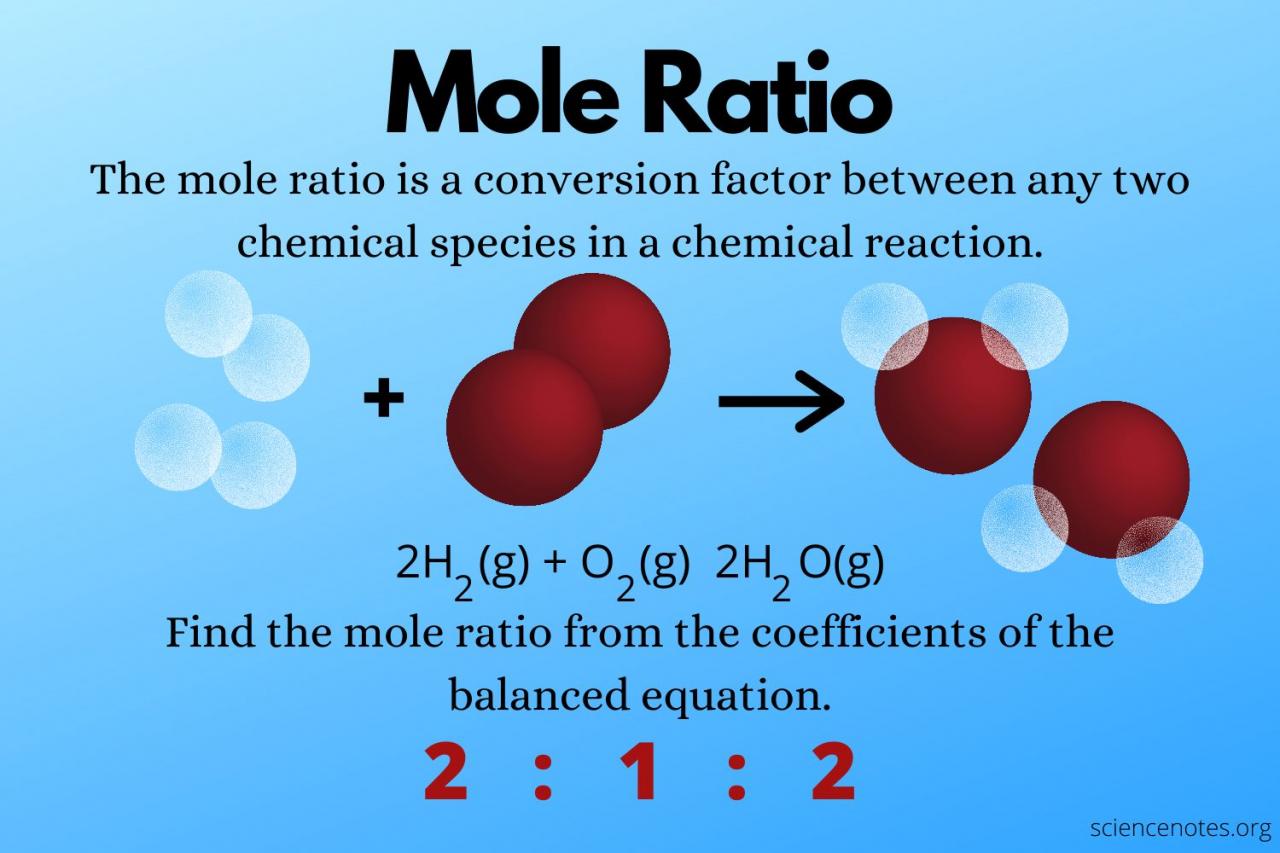
The mole is a fundamental unit of measurement in chemistry, representing a specific amount of a substance. It is defined as the quantity of a substance that contains exactly 6.02214076 × 10^23 elementary entities (atoms, molecules, ions, or electrons).
Mole measurement plays a crucial role in understanding chemical reactions and stoichiometry, as it allows scientists to determine the exact proportions of reactants and products involved in a given reaction. This knowledge is essential for predicting the outcome of chemical reactions and designing experiments.
Methods for Determining Mole Measurement
There are two primary methods for determining the moles of a substance: the gravimetric method and the volumetric method.
Gravimetric Method:This method involves weighing the substance and then using its mass and molar mass to calculate the number of moles. The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of that substance and is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
Volumetric Method:This method involves measuring the volume of a solution containing the substance and then using its concentration and volume to calculate the number of moles. The concentration of a solution is expressed in moles per liter (mol/L).
Applications of Mole Measurement
Mole measurement is widely used in chemical analysis, such as titrations and gravimetric analysis. Titrations involve the controlled addition of a known volume of a solution of known concentration to a solution of unknown concentration. Gravimetric analysis involves determining the mass of a substance after a chemical reaction to calculate the number of moles of the substance.
Mole measurement also plays a vital role in pharmaceutical and industrial chemistry. It is used to determine the purity of chemicals, design new drugs, and optimize chemical processes.
Calculations Involving Mole Measurement
The following table summarizes the formulas and calculations used to convert between mass, volume, and moles of substances:
| Formula | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Moles (n) = Mass (m) / Molar Mass (M) | Calculates the number of moles from the mass and molar mass. |
| Mass (m) = Moles (n) × Molar Mass (M) | Calculates the mass from the number of moles and molar mass. |
| Moles (n) = Volume (V) × Concentration (C) | Calculates the number of moles from the volume and concentration. |
| Volume (V) = Moles (n) / Concentration (C) | Calculates the volume from the number of moles and concentration. |
Errors and Limitations of Mole Measurement
Like any measurement technique, mole measurement can be subject to errors. Potential sources of error include inaccuracies in weighing and measuring, as well as the purity of the substances being measured.
Additionally, mole measurement has limitations. It assumes that the substance being measured is pure and that it does not undergo any chemical reactions during the measurement process. These limitations can affect the accuracy of mole measurements, particularly when dealing with complex or reactive substances.
Outcome Summary
Mole measurement has revolutionized the field of chemistry, enabling scientists to unravel the intricacies of chemical reactions, develop new materials, and advance pharmaceutical research. Its applications extend far beyond the laboratory, impacting industries such as manufacturing, medicine, and environmental science.
As our understanding of the molecular world continues to evolve, mole measurement will remain an indispensable tool for unlocking the secrets of chemistry and shaping the future of science.
FAQ Compilation: Mole Measurement
What is the significance of mole measurement in chemistry?
Mole measurement provides a standardized unit for quantifying the amount of substance, enabling precise calculations and predictions in chemical reactions.
How is mole measurement used in chemical analysis?
Mole measurement is employed in techniques such as titrations and gravimetric analysis to determine the concentration and composition of substances.
What are the potential sources of error in mole measurements?
Inaccuracies in weighing, measuring, and instrument calibration can introduce errors in mole measurements.